ComputerScience & Embedded/NUCLEO & CAN Tranceiver
STM32 HAL and Project Architecture
leecrossun
2025. 3. 1. 14:59
Understanding Project Hierarchy
- Drivers
- CMSIS : CMSIS-CORE layer
- no written by the ST engineers, given by ARM
- written for one of mc (eg. ARM Cortex-Mx) can be used on another mc based on same processor
- it helps develop a portable application across multiple mc
- not for peripherals but for a processor and its associated peripheral (eg. NVIC, SysTick timer, Memory Protection Unit …)
- STM32F4xx_HAL_Driver : STM32-CUBE Layer (STM32Fx_HAL_DRIVER)
- GPIO peripheral driver files which are added by CubeMX software
- CMSIS : CMSIS-CORE layer
- Inc : user application-related header files
- Src : user application-related source files
- startup : startup codes to the project
Project Layers Interaction
- Application code and other source files (main.c)
- take the help of an API which is exposed by the device HAL in order to talk to the peripheral of a microcontroller
- STM32-CUBE Layer(STM32Fx_HAL_DRIVER)
- hal_cortex.c
- provided by the CMSIS layer
- go through CMSIS-CORE when it wants to configure processor specific features
- hal_uart.c
- provided by ST
- hal_cortex.c
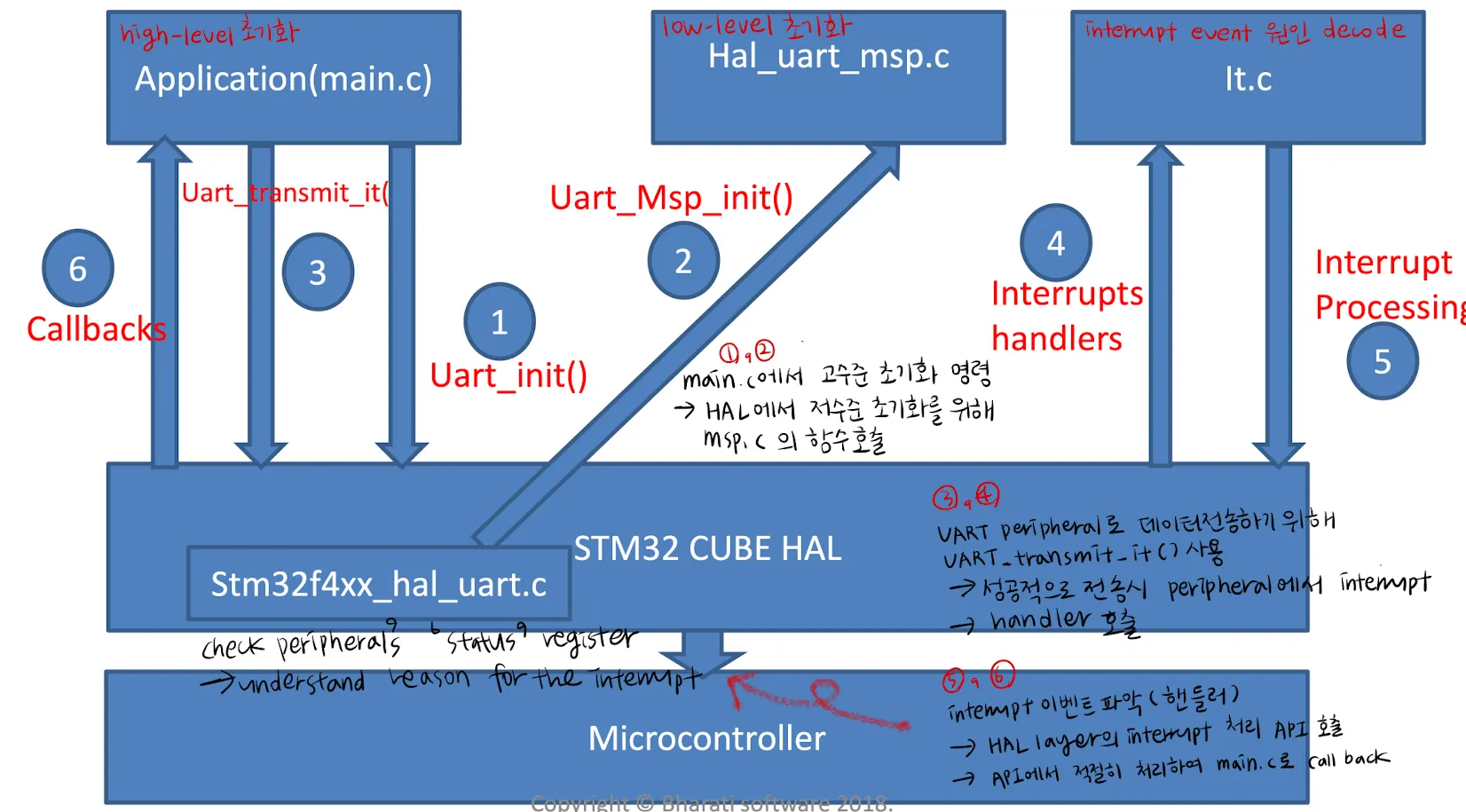
STM32 Cube framework program flow
HAL_UART_Transmit API cannot be called right at the beginning of the main.c
→ Before interacting with any peripherals, it’s important to address several key considerations
💡 Some Mandatory and Optional MCU Inits
- Flash Controller Inits
- Enabling pre-fetch buffer, Data cache, Instruction cache if supported
- Floating point unit inits if supported
- Setting up Stack
- System Clock settings
- HSI - High Speed Internal clock (RC oscillator)
- HSE - High Speed external clock (crystal based oscillator)
- System PLL - Phased Locked Loop engine
- Flash wait state settings when system clock is more
- Systick Timer init to trigger interrupt for every 1ms
- Required when using STM32 HAL APIs
HAL_init()
- Flash Interface Init
- Stm32f4xx_hal_conf.h
- provide configuration required in order to properly init a mc
- provided by the ST’s Cube layer
- Stm32f4xx_hal_conf.h
- SysTick timer init to gernerate interrupt fo 1ms
- Background clock always will be ticking in the Cube Mx generated code (like heartbeat)
- APIs to transmit data over UART, SPI, I2C, CAN (almost all data transfer) actually depend upon this SysTick timer
- Other Processor Specific Low level init
- HSL_MspInit() should be implemented in application layer (msp.c)
- actually to deal with some of the processor level details and this is application specific. So, that's why HAL_Init() actually calls HAL_MspInit()
- Enabling required system exception
- Configuring priority for system exception
- Enabling and configuring other processor features such as MPU, FPU, etc. if required </aside>
- 추가로 찾아본 결과
- HAL은 하드웨어에 의존적이지 않은 인터페이스를 제공하지만, MSP는 하드웨어 설계에 따라 종속적인 초기화 작업을 처리하므로 User Application Layer에 해당 (예: 특정 핀을 UART용 TX/RX로 설정하거나 NVIC를 특정 인터럽트에 대해 활성화하는 작업)
Understanding main.c, msp.c, It.c
반응형